Gulf Stream Weakening Confirmed
The Gulf Stream, a major ocean current, is indeed weakening, and this discovery has significant implications for our planet’s weather systems.
Decades of Data Examined
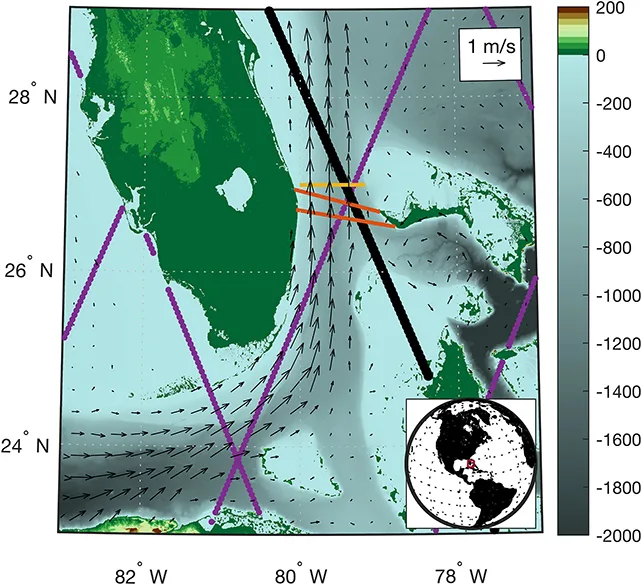
Researchers from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution and the University of Miami have examined four decades of data from the Florida Straits. This data includes measurements of the volume of seawater moving through the region during that time.
A 4 Percent Decline
Their findings reveal that the Gulf Stream’s transport has decreased by approximately 4 percent over the past 40 years. This marks the first “conclusive, unambiguous observational evidence” of a slowdown in the Gulf Stream’s strength.
Uncertain Causes
While the study confirms the weakening, the exact causes were not determined. However, there is a 99 percent likelihood that this weakening is not a random occurrence, according to the researchers.
Complex Data Analysis
A sophisticated Bayesian model was used to analyze data collected from satellite readings, undersea cables, and field recordings. This model calculates probabilities and uncertainties with high precision.
Impacts of the Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream flows from the Gulf of Mexico, around Florida, up the US East Coast, and across the Atlantic. It carries warm water, influencing temperatures, precipitation, sea levels, hurricane activity, and more. It also transports nutrients, including carbon, across the ocean.
Importance of Long-Term Ocean Observations
This study underscores the importance of long-term ocean observations in identifying trends that span several decades or longer.
Climate Change Connection
While it’s clear that the Gulf Stream weakening is likely linked to global warming, the future remains uncertain. The Gulf Stream and its associated weather patterns are critical components of the planet’s climate, affecting extreme weather events, average temperatures, and rainfall.
Feedback Loops and Disruptions
Furthermore, researchers are concerned about how shifts in climate might create feedback loops, leading to further disruptions in weather systems.
Potential for Future Research
The researchers hope that their data analysis technique can be applied to other ocean regions to uncover additional climate change signals.
Global Significance
In the words of oceanographer Lisa Beal from the University of Miami, “The Gulf Stream is a vital artery of the ocean’s circulation, and so the ramifications of its weakening are global.” This discovery highlights the interconnectedness of Earth’s climate systems and emphasizes the need for continued monitoring and research.
Also Read: Discovery: Deepest-Ever Bacteria-Infesting Virus Recovered From Mariana Trench






