Unlocking the Secrets of Quantum Chemistry with Quantum Computers
Observing the Unseen
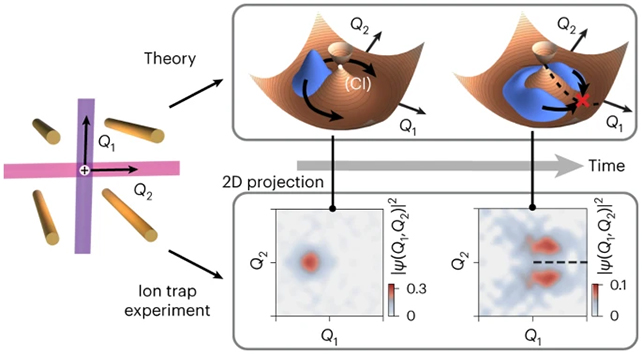
Scientists have achieved a groundbreaking feat in quantum chemistry by using a quantum computer to witness a fundamental interaction that happens too quickly for the human eye to perceive. This interaction, known as a conical intersection, typically occurs in femtoseconds (quadrillionths of a second), making it impossible to directly observe. However, researchers from the University of Sydney in Australia and the University of California, San Diego, devised a clever approach to extend this fleeting moment into a manageable timeframe.
Also Read: What Do Ocean Animals Experience During A Hurricane?
Slowing Down Time
The research team slowed down the chemical reaction by trapping a charged particle in a field and monitoring its behavior. With the help of their quantum computer, they stretched the process from femtoseconds to milliseconds, allowing them to make meaningful observations and measurements. This achievement marks the first time such an observation has been made.
Deciphering Conical Intersections
Conical intersections involve the rapid exchange of energy between potential energy surfaces within molecules. These intricate interactions are best understood through the principles of quantum physics, which involve the overlap of fields and the changing behavior of particles. In practical terms, quantum reactions govern essential processes like photosynthesis and the reactions occurring in the human eye.
The Quantum Computer Advantage
What set this research apart was the innovative method the scientists used to map changes in electron states onto a system. They employed a trapped ion quantum computer, harnessing electric fields for trapping and lasers for manipulation. This complex procedure allowed them to slow down and observe the otherwise elusive conical intersection. Think of it as studying aerodynamics on an airplane wing in a wind tunnel.
A Leap in Scientific Understanding
Conical intersections are prevalent in photochemistry, making this research invaluable for various scientific fields. It highlights the power of interdisciplinary collaboration, where experts from different scientific domains work together to uncover new insights.
Quantum Computing’s Potential
This breakthrough underscores the potential of quantum computers in simulating a wide array of reactions and interactions. By gaining a deeper understanding of these ultrafast and minuscule events, we open doors to advancements in materials science, drug design, and solar energy harvesting.
Impacts Beyond Chemistry
Moreover, this newfound knowledge can also impact processes involving molecules interacting with light, such as the formation of smog or the depletion of the ozone layer. Understanding these fundamental processes may pave the way for innovative solutions to environmental challenges.
In essence, this groundbreaking research not only sheds light on the mysteries of quantum chemistry but also showcases how collaboration and cutting-edge technology can revolutionize our understanding of the world around us, leading to exciting possibilities in various scientific endeavors.
The research has been published in Nature Chemistry.






